Diabetes Home Test Kit
Some people may have very clear symptoms of diabetes, but many people are not aware that they are at risk of developing diabetes. Taking a home diabetes test is a quick and reliable way of knowing if you are predisposed to developing diabetes.
Why Use A Home Diabetes Test?
There are different types of diabetes, the main two being type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. In all types of diabetes however the main issue is that glucose can’t get into your cells properly, so it begins to build up in your blood. Common symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst, increased urination, feeling tired and losing weight-when you are not trying to. Some of these symptoms can be really hard to spot and, in many cases, type 2 diabetes is diagnosed when you are having a blood test for something else. So, taking a home diabetes test could confirm if you are at risk of developing diabetes.
Who Should Use A Home Diabetes Test?
If you have any of the symptoms of diabetes including urinating more than usual, constantly feeling thirsty, tiredness, itchy skin, unexplained weight loss, dry mouth and dry eyes then you should consider taking a test to see if you are at risk of developing diabetes. In addition, you may have already been diagnosed with diabetes but want to know how well you are controlling it.
What’s In A Home Test Kit?
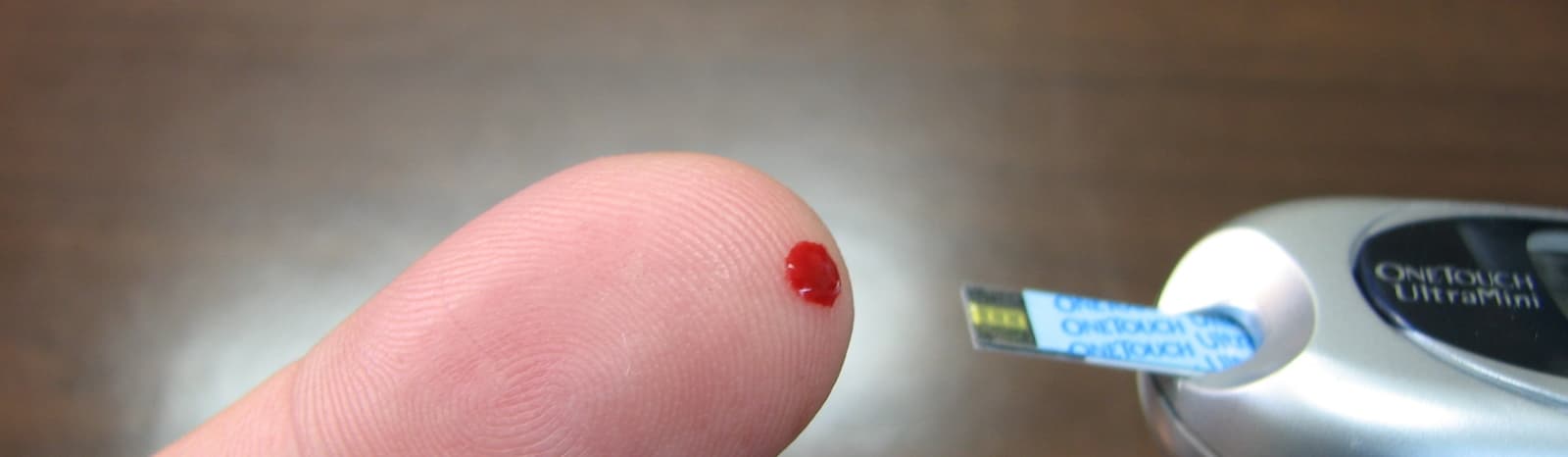
A finger prick blood sample is required so in the test pack you should find lancets, a blood spot card, blood collection vials, complete with detailed information on how to take the test.
What Does A Home Diabetes Test Do?
Most diabetes home tests will test your levels of HbA1c, which is glycated haemoglobin. This is what’s made when the glucose in your body sticks to your red blood cells. Your body can’t use the sugar properly so more of it builds up in your blood. A high HbA1c means you have too much sugar in your blood. Different measurements can indicate if you have prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. With most tests if you are less than 5.7% then your blood glucose is in the normal range, 5.7-6.5% you may have a risk of developing diabetes and more than 6.5% you have high levels of glucose in your blood and should consult your doctor. You may, on the basis of your results, be advised to seek medical advice.
